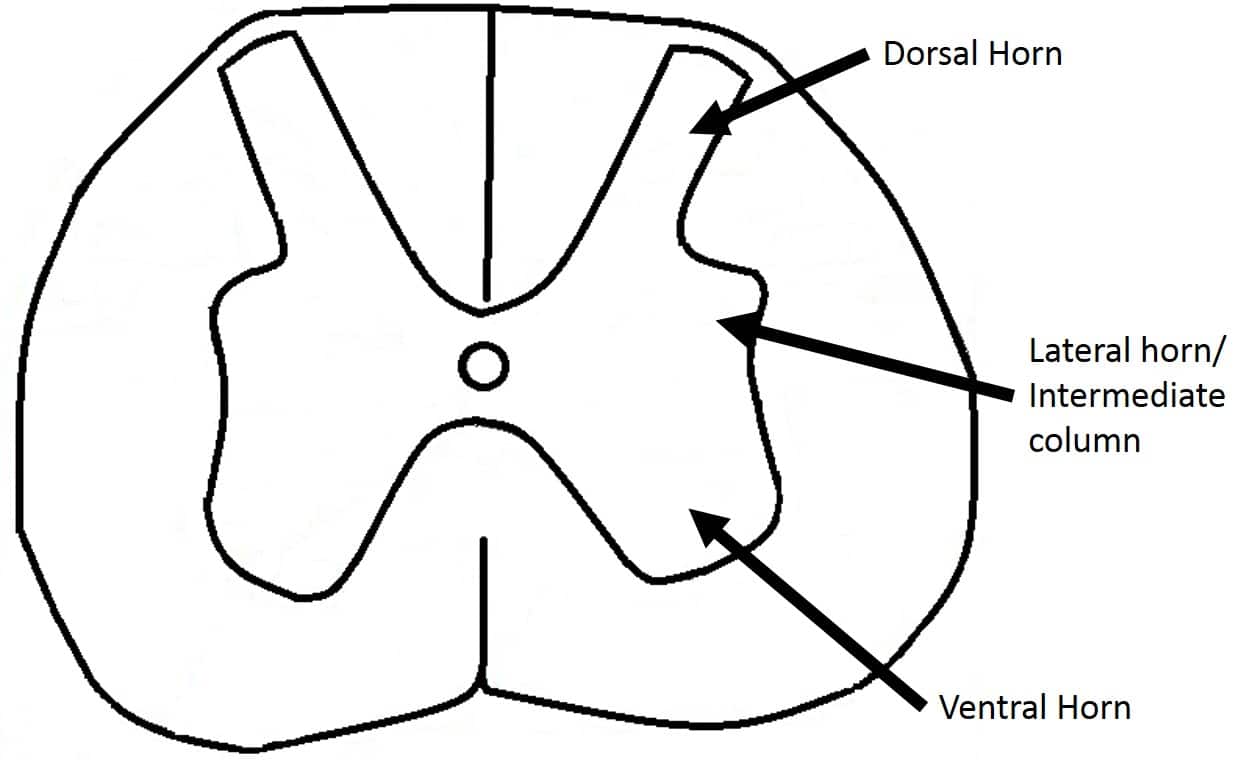
It receives several types of sensory information from the body. The dorsal horn the intermediate column the lateral horn and the ventral horn.

Dorsal Horn Anatomy Britannica
It contains the substantia gelatinosa.

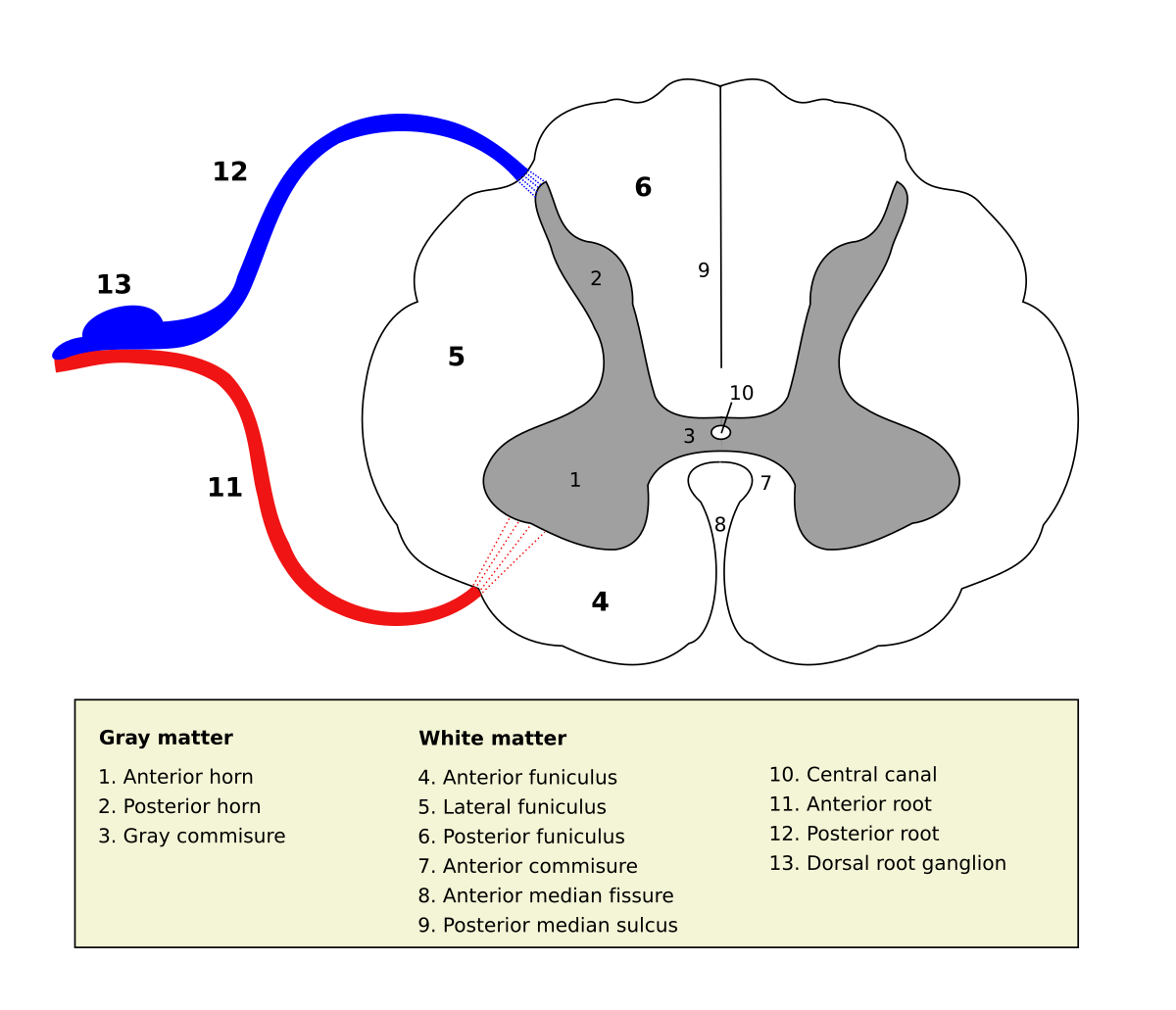
. The grey matter is divided into four main columns. In transverse sections the gray matter is conventionally divided into dorsal posterior lateral and ventral anterior horns The neurons of the dorsal horns receive sensory information that enters the spinal cord via the dorsal roots of the spinal nerves. The nuclei of the posterior horn are the marginal nucleus TA nucleus marginalis TA gelatinous substance TA substantia gelatinosa TA nucleus proprius TA secondary visceral grey substance TA.
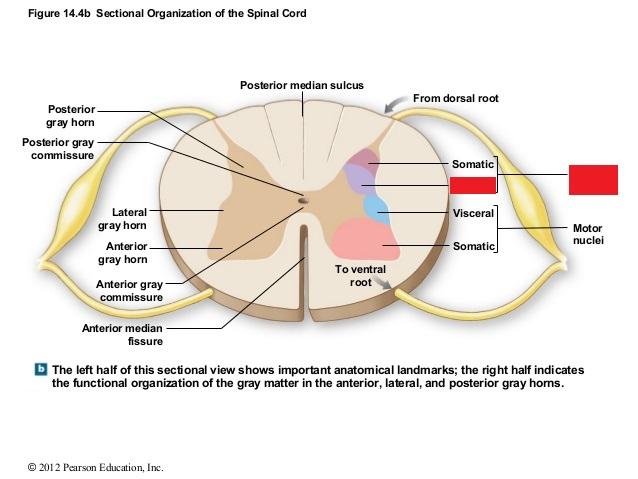
The functional organization of the gray matter in the anterior lateral and posterior gray horns. Spinal Cord Gray Matter Functions. It receives several types of sensory information from the body including fine touch proprioception and vibration.
Sensory nuclei- somatic and visceral -receives information from skeletal muscles and skin somatic and visceral organs visceral and relays it to CNS. The gray matter is the area of the spinal cord where many types of neurons synapse. The lateral horn which is only found in the thoracic upper lumbar and sacral regions is the central component of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.
Posterior gray horn Posterior gray commissure Lateral gray horn Anterior gray horn Anterior gray commissure Anterior median fissure To ventral root Posterior median sulcus From dorsal root Sensory nuclei Motor nuclei Somatic Somatic Visceral Visceral. The posterior grey column posterior cornu dorsal horn spinal dorsal horn posterior horn sensory horn of the spinal cord is one of the three grey columns of the spinal cord. It contains the substantia gelatinosa.
One of the divisions of the grey matter of the spinal cord the posterior horn contains interneurons that make connections within the spinal cord as well as neurons that enter ascending sensory pathways. Gray Horns The posterior horn is responsible for sensory processing. It receives various types of sensory information from the body including light touch proprioception and vibration.
The posterior grey column posterior cornu dorsal horn spinal dorsal horn posterior horn sensory horn of the spinal cord is one of the three grey columns of the spinal cord. The anterior grey column is the column where the cell bodies of alpha motor neurons are located. The posterior horn receives the sensory information from receptors of the bones joints and skin through sensory nerve cells whose cell bodies are located in the dorsal root ganglion which is a.
Posterior part of gray matter Function. The posterior horn TA or dorsal horn TAalt contains spinal laminae I-VI TA of Rexed. The anterior horn sends out motor signals to the skeletal muscles.
The anterior grey column contains motor neurons that affect the skeletal muscles while the posterior grey column receives information regarding touch and sensation. One of the divisions of the grey matter of the spinal cord the posterior horn contains interneurons that make connections within the spinal cord as well as neurons that enter ascending sensory pathways. Spinal Cord Internal Structure- Gray matter.
As shown in Figure 1441 the gray matter is subdivided into regions that are referred to as horns. The posterior horn or gray column of the spinal cord as appearing in cross section. In cross-sections the spinal cord consists of a central butterfly-shaped zone of gray matter and an outer rim of white matter.
The posterior horn posterior horn dorsal horn spinal dorsal horn of the spinal cord is the dorsal more posterior gray matter of the spinal cord. The ventral horn also known as the. The lateral grey column receives input signals from preganglionic myelinated fibers from viscera internal organs which course through prevertebral ganglia between the visceral organ and the sympathetic chain and paravertebral ganglia in the sympathetic chain white rami communicantes and dorsal roots to synapse on cells of the intermediolateral cell column in.
The dorsal posterior horn neurons receive incoming afferent sensory signals while the ventral anterior horn neurons. The dorsal horn also known as the posterior horn contains neurons that receive somatosensory information from the body which is then transmitted via the ascending pathways to the brain. The posterior horn is responsible for sensory processing.
The lateral horn which is only found in the thoracic upper lumbar and sacral regions is the central component of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. It is one of the three grey columns. What is the dorsal column medial lemniscus pathway.
The anterior horn sends out motor signals to the skeletal muscles. It receives several kinds of physical information in the body including light touch proprioception and vibration. Gray Horns The posterior horn is responsible for sensory processing.
Contents 1 Structure 2 Clinical significance. The posterior horn posterior cornu dorsal horn spine dorsal horn from the spinal-cord may be the dorsal more for the back gray few the spinal-cord. The anterior horn sends out motor signals to the skeletal muscles.
In the dorsal horns or posterior horns many incoming sensory neurons synapse with interneurons which then distribute information to other parts of the spinal cord and brain.

Lab 8 Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet

14 4 The Spinal Cord Anatomy Physiology

0 comments
Post a Comment